Research uses ‘smart score’ to rank appeal of Aussie places to migrants

New Victoria University research has ranked more than 100 Australian cities and towns with a ‘smart score’ based on their economy, environment, governance, mobility, liveability, and people.
Using Australian Bureau of Statistics and other government data sources, and a form of statistical analysis known as analytical hierarch processing, the study aims to identify links between a city’s smart score and people’s preference to live there.
It shows most capital cities outrank regional centres, and they are also the locations that tend to attract new residents. The research suggests that it is important to develop the regional centres if the government wants to reduce the pressure of concentrated migration trends to mega cities.
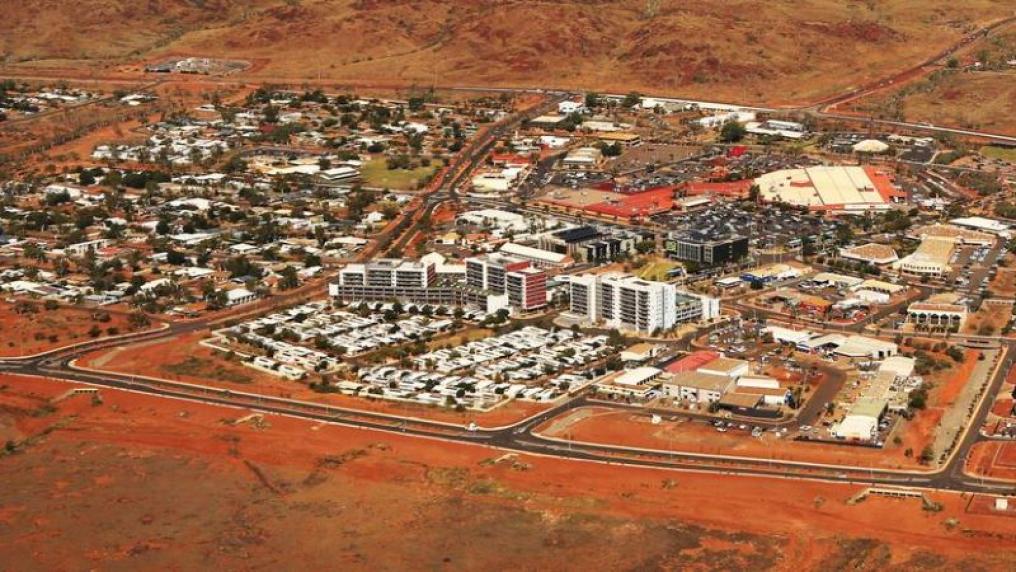
The ACT led the list, followed by Sydney, Melbourne, Darwin, Perth, and Brisbane. Karratha in WA, followed by Newcastle in NSW, were the top regional cities, ranking higher than state capitals Adelaide and Hobart.
The lowest performing town was Rockhampton in Queensland, but a cluster of South Australian towns, including Mount Gambier, Port Lincoln, Victor Harbour, Port Augusta and Whyalla were also at the bottom.
Author Maha Hussein, who conducted the analysis as an undergraduate student in the College of Engineering and Science under the co-supervision of Dr Muhammad Atiq Tariq, said the paper may provide evidence that government migration programs to settle newcomers outside major cities are not as successful as they could be.
Research could be tool to manage migrant settlement
"Developing a connection between how ‘smart’ a place is and its ability to attract human capital was a relatively novel hypothesis, and our research affirmed a strong correlation. This research could be a tool to address the challenges of developing regional centres,” she said.
The factors the study analysed included:
- entrepreneurship, business infrastructure, and productivity under Economy
- participation, community engagement, and government funding under Governance
- energy initiatives, environmental management, renewable energy initiatives, and pollution and water indexes under Environment
- affordable housing, employment opportunities, and indexes for safety, health and income under Liveability
- public transport, road networks, and accessibility under Mobility
- cultural awareness, active lifestyle and voter participation under People.
The research, Smart City Ranking System: A Supporting Tool to Manage Migration Trends for Australian Cities was recently published in the MDPI publication, Infrastructures.
Dr Tariq introduced a new culture in Victoria University by motivating undergraduate students to publish their work in high-rank journals through quality research. This is the fifth research paper published under his mentorship from the same undergraduate batch of Civil Engineering students.